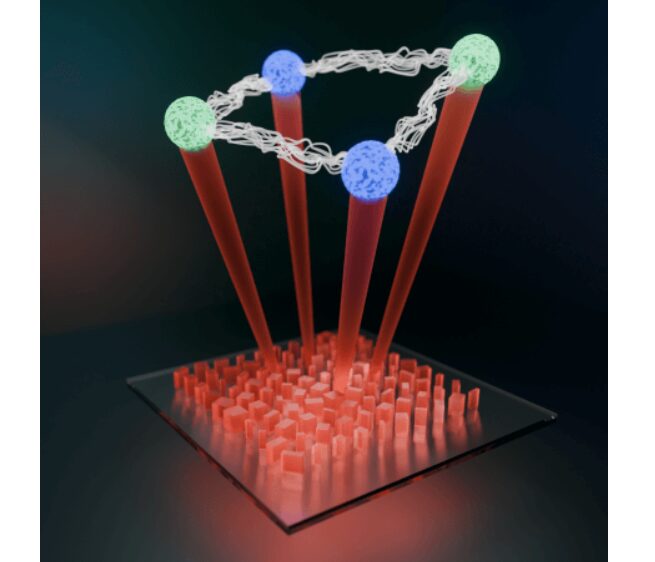
In the race toward practical quantum computers and networks, photons hold intriguing possibilities as fast carriers of information at room temperature.
Photons are typically controlled and coaxed into quantum states via waveguides on extended microchips, or through bulky devices built from lenses, mirrors, and beam splitters. The photons become entangled—enabling them to encode and process quantum information in parallel—through complex networks of these optical components. But such systems are notoriously difficult to scale up due to the large numbers and imperfections of parts required to do any meaningful computation or networking.
Could all those optical components be collapsed into a single, flat, ultra-thin array of subwavelength elements that control light in the exac...
Read More






Recent Comments