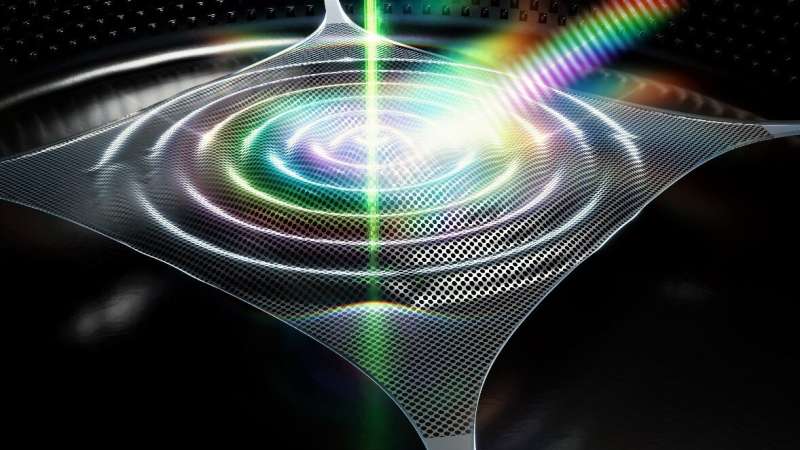
Physicists at Delft University of Technology have built a new technology on a microchip by combining two Nobel Prize-winning techniques for the first time. This microchip could measure distances in materials at high precision—for example, underwater or for medical imaging.
Because the technology uses sound vibrations instead of light, it is useful for high-precision position measurements in opaque materials. The instrument could lead to new techniques to monitor the Earth’s climate and human health. The work is now published in Nature Communications.
Simple and low-power technolog...
Read More






Recent Comments