
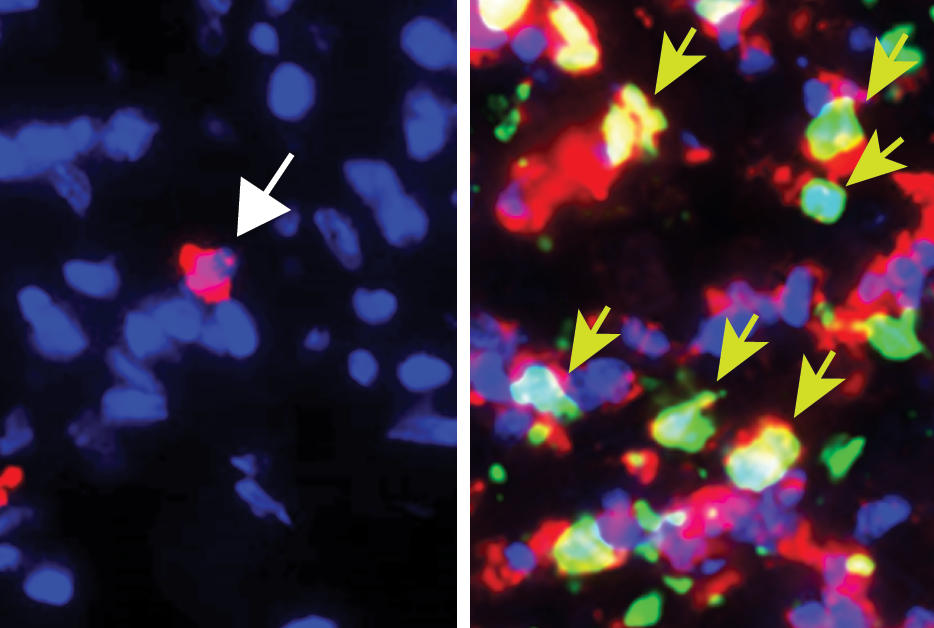
Immune cells released from bone marrow in the skull in response to chronic stress and adversity could play a key role in symptoms of depression and anxiety, say researchers.
The discovery—found in a study in mice—sheds light on the role that inflammation can play in mood disorders and could help in the search for new treatments, in particular for those individuals for whom current treatments are ineffective.
Around 1 billion people will be diagnosed with a mood disorder such as depression or anxiety at some point in their life...
Read More






Recent Comments