New radio astronomy observations of a planetary system in the process of forming show that once the first planets form close to the central star, these planets can help shepherd the material to form new planets farther out. In this way each planet helps to form the next, like a line of falling dominos each triggering the next in turn.
To date over 5000 planetary systems have been identified. More than 1000 of those systems have been confirmed to host multiple planets. Planets form in clouds of gas and dust known as protoplanetary disks around young stars. But the formation process of multi-planet systems, like our own Solar System, is still poorly understood.
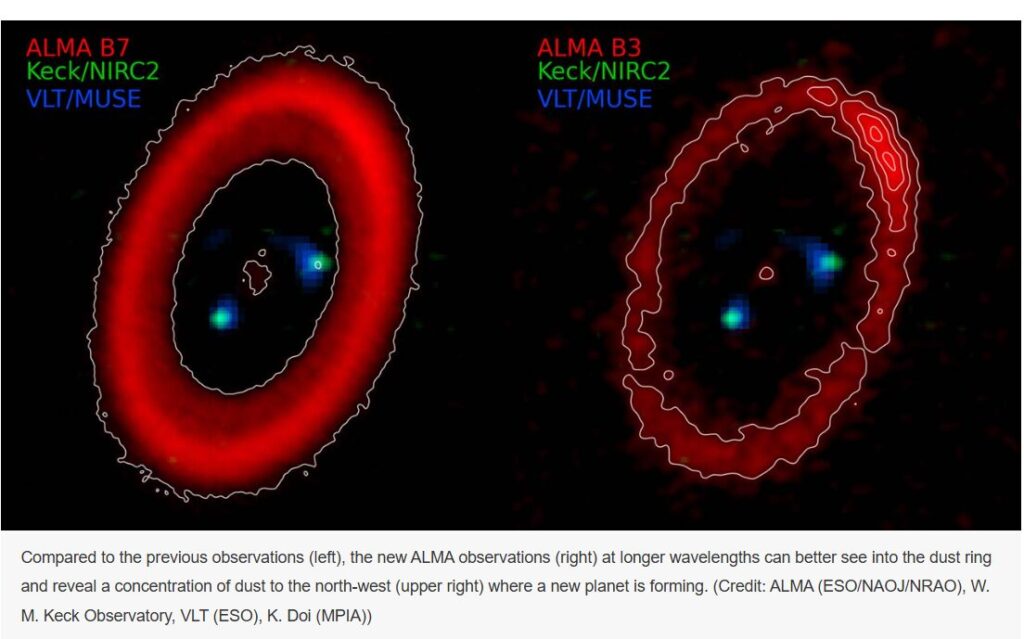
The best example object to study multi-planet system formation is a young star known as PDS 70, located 367 light years a...
Read More





Recent Comments