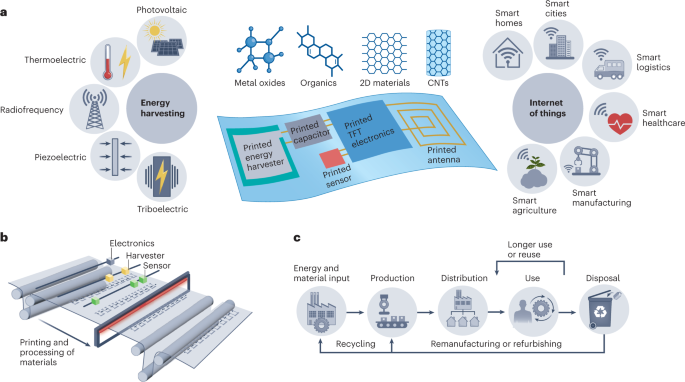
Creating smart sensors to embed in our everyday objects and environments for the Internet of Things (IoT) would vastly improve daily life — but requires trillions of such small devices. Simon Fraser University professor Vincenzo Pecunia believes that emerging alternative semiconductors that are printable, low-cost and eco-friendly could lead the way to a cheaper and more sustainable IoT.
Leading a multinational team of top experts in various areas of printable electronics, Pecunia has identified key priorities and promising avenues for printable electronics to enable self-powered, eco-friendly smart sensors. His forward-looking insights are outlined in his paper published on Dec. 28 in Nature Electronics.
“Equipping everyday objects and envir...
Read More





Recent Comments