
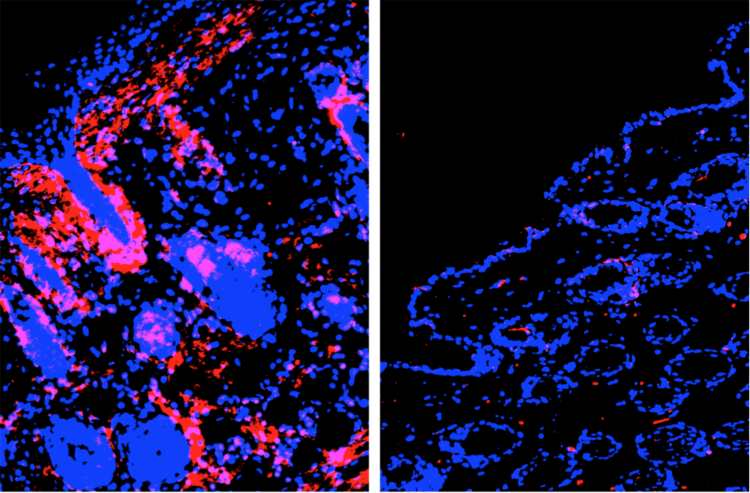
Scientists at The Wistar Institute have identified a previously overlooked mediator in the body’s response to life-threatening infections: hippuric acid, a metabolite produced when gut bacteria break down polyphenols from berries, tea, and other plant-based foods. The research reveals that this molecule acts as an immune-system amplifier, boosting the body’s inflammatory defenses during early infection but elevating them to deadly levels when infections progress to sepsis.
Published in Cell Reports, the study demonstrates that elevated hippuric acid levels correlate with increased mortality in sepsis patients, while also uncovering the molecular mechanisms by which this metabolite modifies immune re...
Read More






Recent Comments