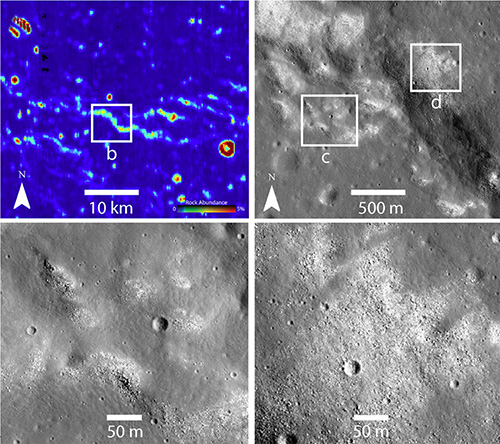
Researchers have discovered a system of ridges spread across the nearside of the Moon topped with freshly exposed boulders. The ridges could be evidence of active lunar tectonic processes, the researchers say, possibly the echo of a long-ago impact that nearly tore the Moon apart.
“There’s this assumption that the Moon is long dead, but we keep finding that that’s not the case,” said Peter Schultz, a professor in Brown University’s Department of Earth, Environmental and Planetary Sciences and co-author of the research, which is published in the journal Geology...
Read More







Recent Comments