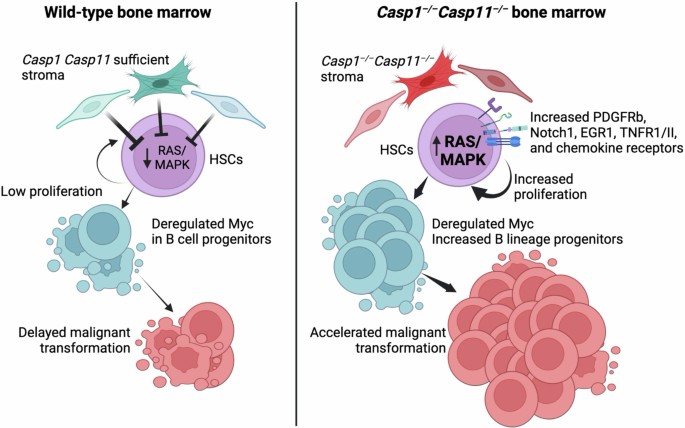
A group of immune proteins called the inflammasome can help prevent blood stem cells from becoming malignant by removing certain receptors from their surfaces and blocking cancer gene activity, according to a preclinical study by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators.
The study, published in Nature Immunology, may lead to therapies that target the earliest stages of cancer. The findings bolster the idea that the inflammasome has a dual role: It promotes inflammation associated with poor outcomes in late cancer stages, but early on, it can help prevent cells from becoming cancerous in the first place.
“What was striking was that the in...
Read More






Recent Comments