A new study led by researchers from Oxford University, Southwest Research I...
Read Moresubsurface ocean tagged posts
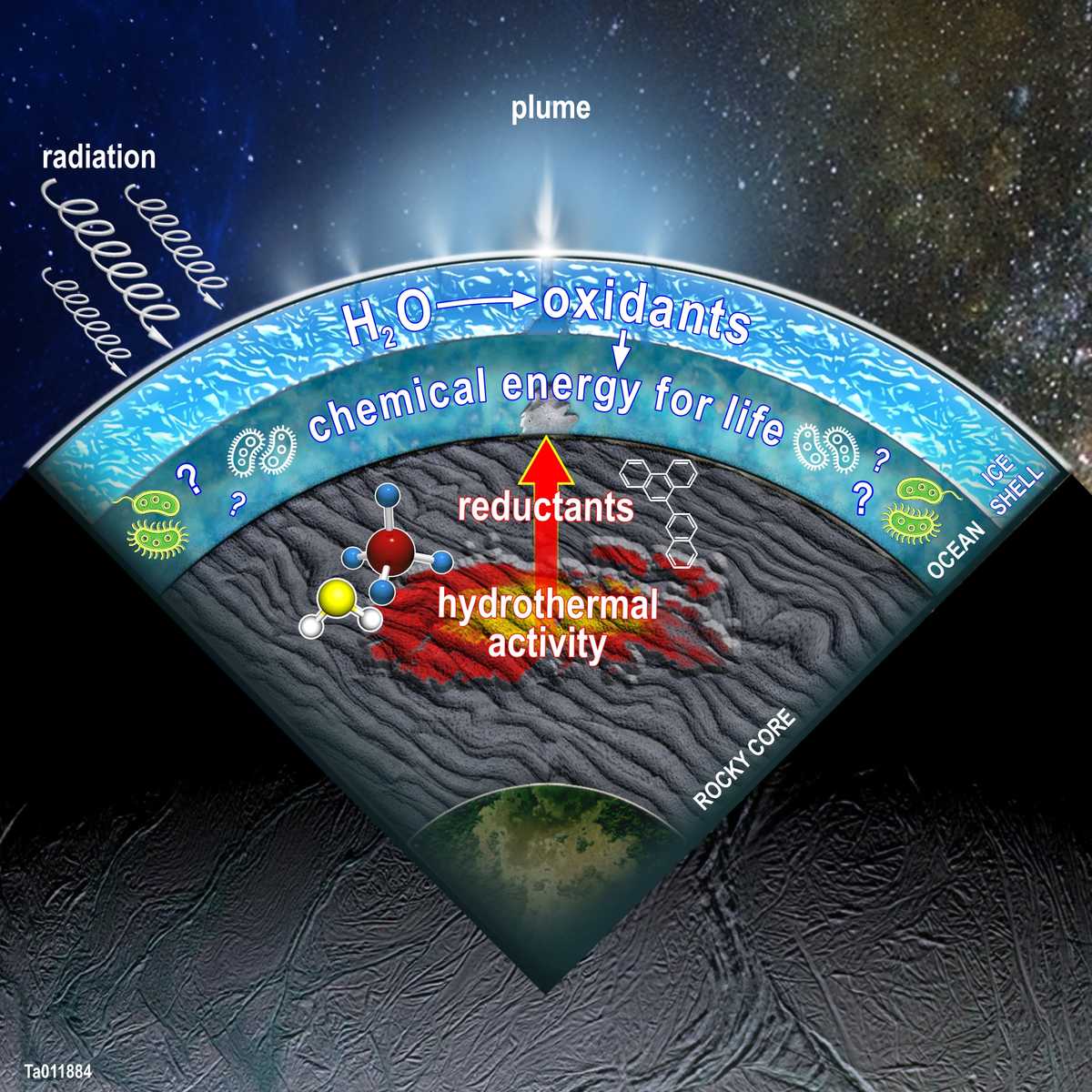
Using data from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, scientists at Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) modeled chemical processes in the subsurface ocean of Saturn’s moon Enceladus. The studies indicate the possibility that a varied metabolic menu could support a potentially diverse microbial community in the liquid water ocean beneath the moon’s icy facade.
Prior to its deorbit in Sep...
Read More
Ralph Instrument Pluto Maps. New Horizons not only showed humanity what Pluto looks like, but also provided information on the composition of Pluto’s atmosphere and surface. These maps — assembled using data from the Ralph instrument — indicate regions rich in methane (CH4), nitrogen (N2), carbon monoxide (CO) and water (H2O) ices. Sputnik Planitia shows an especially strong signature of nitrogen near the equator. SwRI scientists combined these data with Rosetta’s comet 67P data to develop a proposed “giant comet” model for Pluto formation. Credit: Image Courtesy of NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Southwest Research Institute
New Horizons, Rosetta data fusion points to new theory...
Read More




Recent Comments