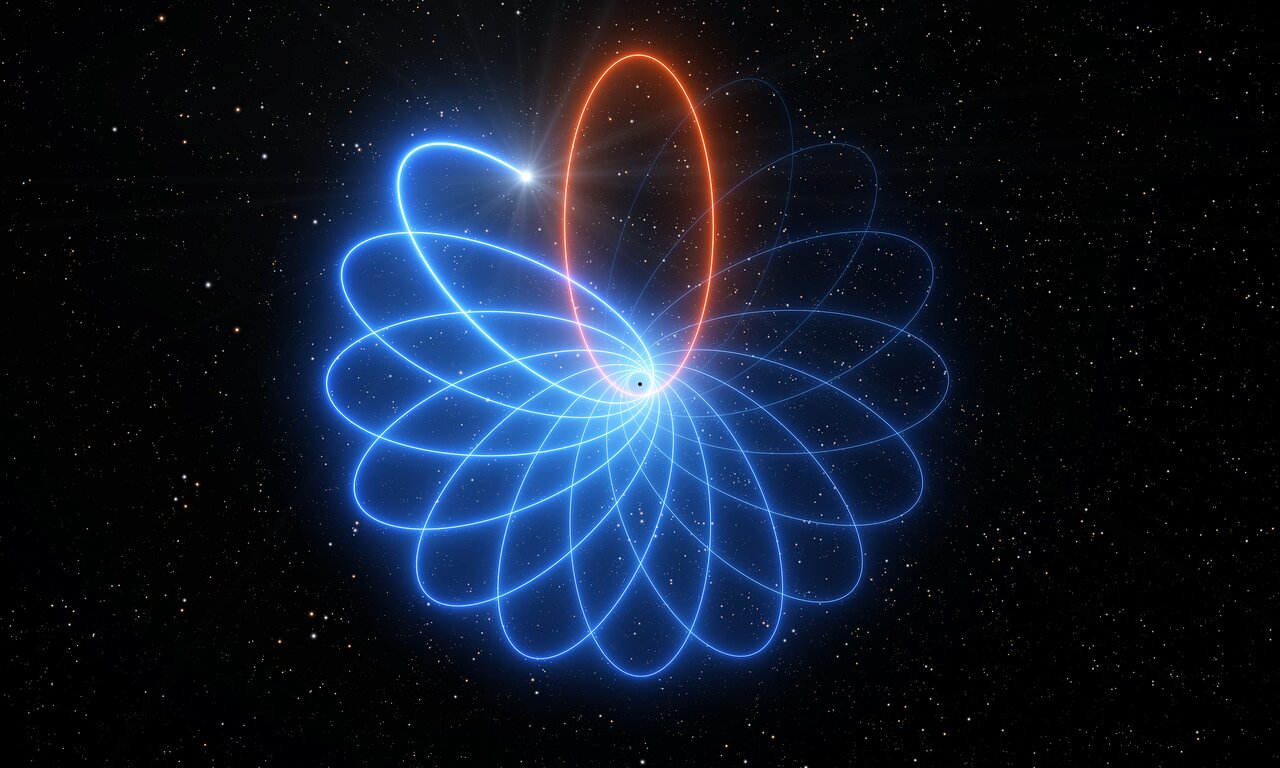
Observations made with ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) have revealed for the first time that a star orbiting the supermassive black hole at the centre of the Milky Way moves just as predicted by Einstein’s general theory of relativity...
Read More

Observations made with ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) have revealed for the first time that a star orbiting the supermassive black hole at the centre of the Milky Way moves just as predicted by Einstein’s general theory of relativity...
Read More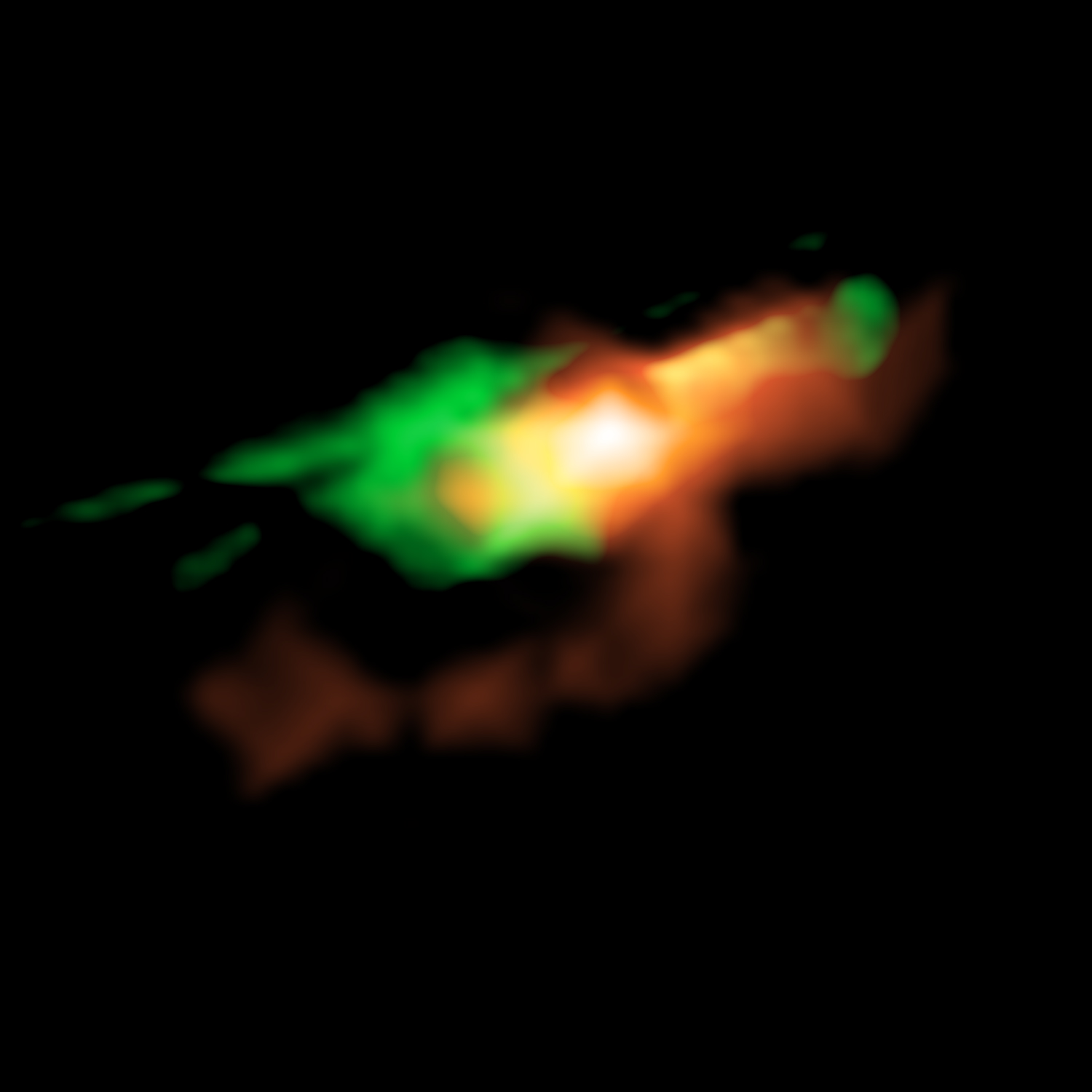
Astronomers obtained the first resolved image of disturbed gaseous clouds in a galaxy 11 billion light-years away by using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA). The team found that the disruption is caused by young powerful jets ejected from a supermassive black hole residing at the center of the host galaxy. This result will cast light on the mystery of the evolutionary process of galaxies in the early Universe.
It is commonly k...
Read More
New ALMA observations reveal a never-before-seen disk of cool, interstellar gas wrapped around the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way...
Read More
Images reveal supermassive black hole at the heart of the Messier 87 galaxy. An international team of over 200 astronomers, including scientists from MIT’s Haystack Observatory, has captured the first direct images of a black hole...
Read More
Recent Comments