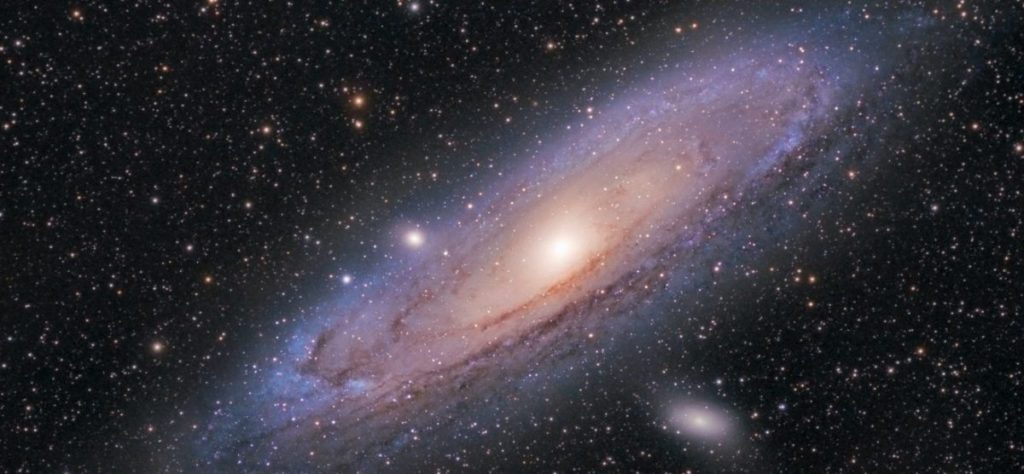

Black holes are regions of space where gravity is so strong that nothing can escape. New research is examining the radiation and winds emanating from black hole activity and shows how they may exert effects on nearby planets.
“The impact of AGN outflows on the surface habitability of terrestrial planets in the Milky Way” is a research paper by the team of astrobiologist Manasvi Lingam and astrophysicist Eric Perlman from Florida Tech’s Department of Aerospace, Physics and Space Sciences, as well as researchers from the University of Rome, University of Maryland and Goddard Space Flight Center...
Read More






Recent Comments