Led by researchers from Université de Montréal’s Trottier Institute for Research on Exoplanets (iREx), a team of astronomers has harnessed the power of the revolutionary James Webb Space Webb Telescope (JWST) to study the “hot Saturn” exoplanet HAT-P-18 b.
Their findings, published last month in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, paint a complete picture of the HAT-P-18 b’s atmosphere while exploring the great challenge of distinguishing its atmospheric signals from the activity of its star.
HAT-P-18 b is located over 500 light-years away with a mass similar to Saturn’s but a size closer to that the larger planet Jupiter. As a result, the exoplanet has a “puffed-up” atmosphere that is especially ideal for analysis.
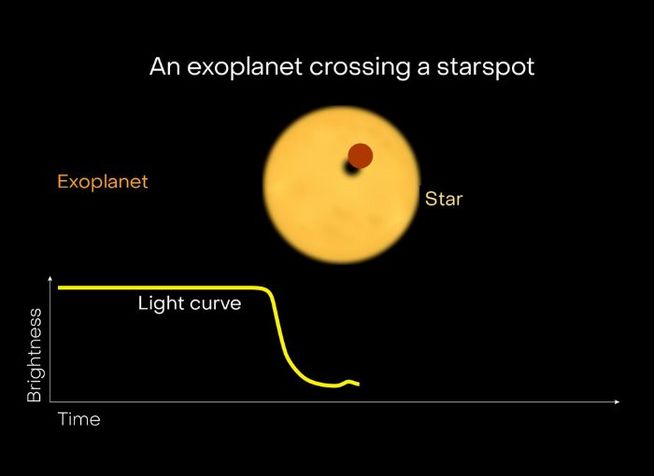
Passing over a spotted star
Read More





Recent Comments