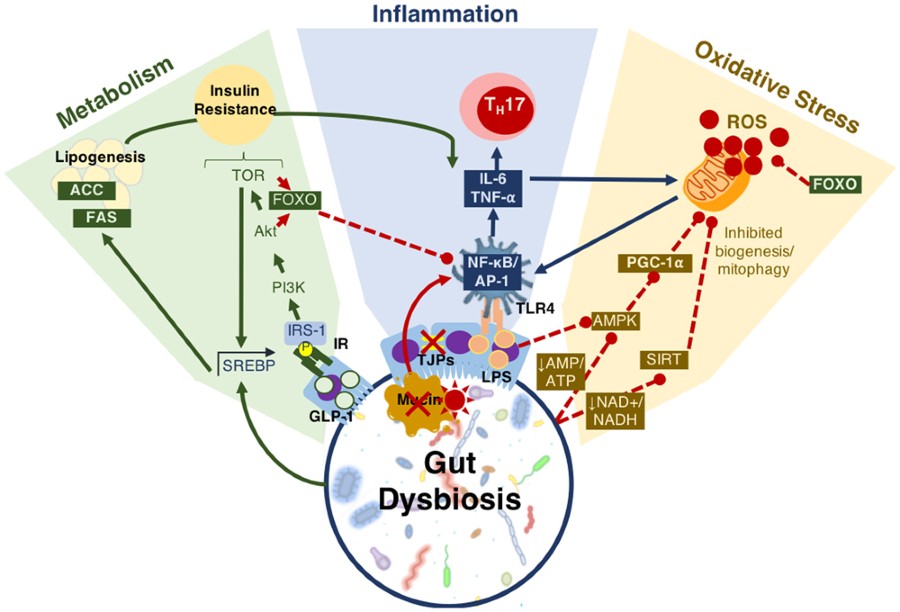
Model of mechanisms of gut microbiota-host communication influencing aging factors. The gut microbiota communicates with the metabolic, inflammatory and oxidative stress pathways via direct and indirect mechanisms. As the physiological changes in all three of these axes are cross-regulatory, the simultaneous action implemented by the gut microbiota makes it a powerful influence in aging and age-related chronic disease development...





Recent Comments