One of the main waste by-products of the biodiesel industry, glycerol, can be used as a raw material for the generation of valuable dihydroxyacetone and hydrogen, the latter of which can be used as 100% clean fuel.
Scientists develop a cheap and efficient copper-based catalyst that can be used to convert glycerol, one of the main by-products of the biodiesel industry, into a valuable compound called dihydroxyacetone. In addition, this same process produces hydrogen molecules from water, and these could be used as a clean type of fuel, further highlighting the impact of this research in terms of energy sustainability.
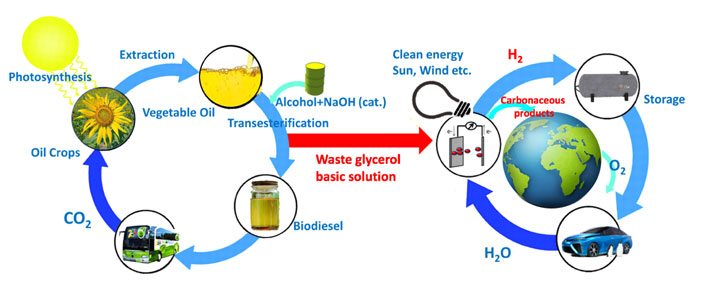
Hydrogen (H2) is a very attractive candidate as a replacement of fossil fuels because it can be produced from water (H2O) through hydrolysis, the splitting of water molecules. Another sustainable route is the synthesis of biodiesels, which are made using vegetable oils through a transformation process known as transesterification. However, biodiesel synthesis produces excessive amounts of glycerol (C3H8O3); it is estimated than the biodiesel industry in Europe alone produces a surplus of 1.4 million tons of glycerol, which cannot be sold to other industries. If glycerol could be used as a raw material to obtain more valuable chemicals, this would make the biodiesel industry more profitable, thus encouraging governments and companies to switch away from fossil fuels.
Fortunately, researchers from Tokyo Tech and Taiwan Tech recently found an efficient way to put this surplus glycerol to good use. While the electrochemical conversion of glycerol to other more valuable organic compounds, such as dihydroxyacetone (DHA), has been studied for years, existing approaches require the use of precious metals, namely platinum, gold, and silver. Because the use of these metals represents 95% of the overall cost of glycerol to DHA conversion, this research team focused on finding an affordable alternative.
In their study, they found that copper oxide (CuO), a cheap and abundant material, could be used as a catalyst to selectively convert glycerol into DHA even at mild reaction conditions. For this to happen, the pH (concentration of free hydrogen ions) in the solution of the electrochemical cell has to be at a specific value. Through various microscopy techniques, the researchers analyzed the crystalline structure and composition of the CuO catalyst and tailored them to make it stable while also carefully inspecting the possible conversion pathways for glycerol in their system according to the solution’s pH. This allowed them to find appropriate reaction conditions that favored the production of DHA. “We have not only discovered a new, earth-abundant catalyst for high-selectivity DHA conversion, but also demonstrate the possibility of giving new valuable life to a waste product of the biodiesel industry,” remarks Prof. Tomohiro Hayashi, lead researcher from Tokyo Tech.
What’s more, the electrochemical system proposed in this study not only produced DHA from glycerol on one end, but also H2 on the other through water splitting. This means that this approach could be used to address two current problems simultaneously. “Both the biodiesel and the hydrogen generation industries could benefit from our system, leading to a more sustainable world,” explains Prof. Hayashi. https://www.titech.ac.jp/english/news/2020/046055.html






Recent Comments