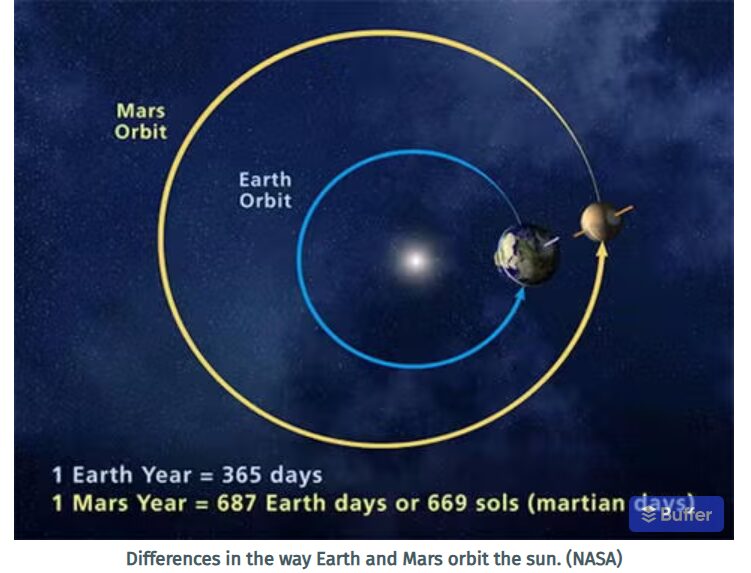
At half the size of Earth and one-tenth its mass, Mars is a featherweight as far as planets go. Yet new research reveals the extent to which Mars is quietly tugging on Earth’s orbit and shaping the cycles that drive long-term climate patterns here, including ice ages.
The study is published in the journal Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific.
Stephen Kane, a professor of planetary astrophysics at UC Riverside, began this project with doubts about recent studies tying Earth’s ancient climate patterns to gravitational nudges from Mars. These studies suggest that sediment layers on the ocean floor reflect climate cycles influenced by the red planet despite its distance from Earth and small size.
“I knew Mars had some effect on Earth, but I assumed it was tiny,...
Read More






Recent Comments