Credits:Image: Courtney Yaeger and Mark Harnet
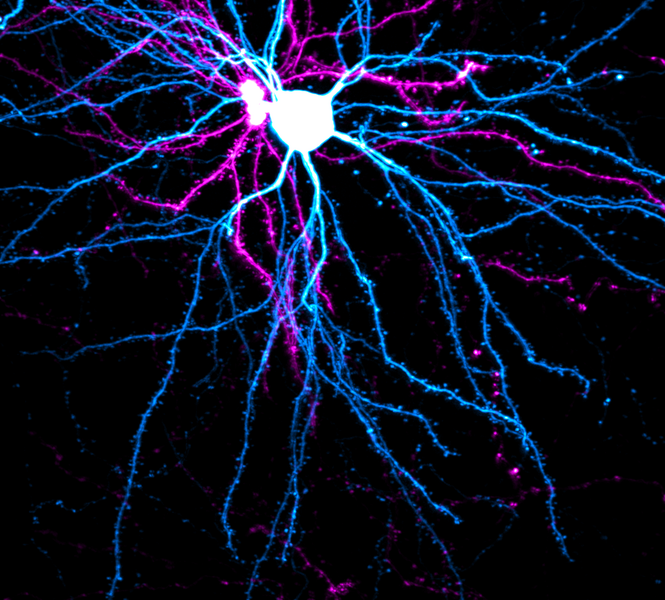
One of the brain’s most celebrated qualities is its adaptability. Changes to neural circuits, whose connections are continually adjusted as we experience and interact with the world, are key to how we learn. But to keep knowledge and memories intact, some parts of the circuitry must be resistant to this constant change.
“Brains have figured out how to navigate this landscape of balancing between stability and flexibility, so that you can have new learning and you can have lifelon...
Read More








Recent Comments