
Category Biology/Biotechnology

A stem cell treatment helped improve the motor function of two out of four patients with a spinal cord injury in the first clinical study of its kind, Japanese scientists said.
There is currently no effective treatment for paralysis caused by serious spinal cord injuries, which affect more than 150,000 patients in Japan alone, with 5,000 new cases each year.
Researchers at Tokyo’s Keio University are conducting their study using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS)—created by stimulating mature, already specialized, cells back into a juvenile state.
They can then be prompted to mature into different kinds of cells, with the Keio researchers using iPS-derived cells of the neural stem.
The university said on Friday that the motor function s...
Read More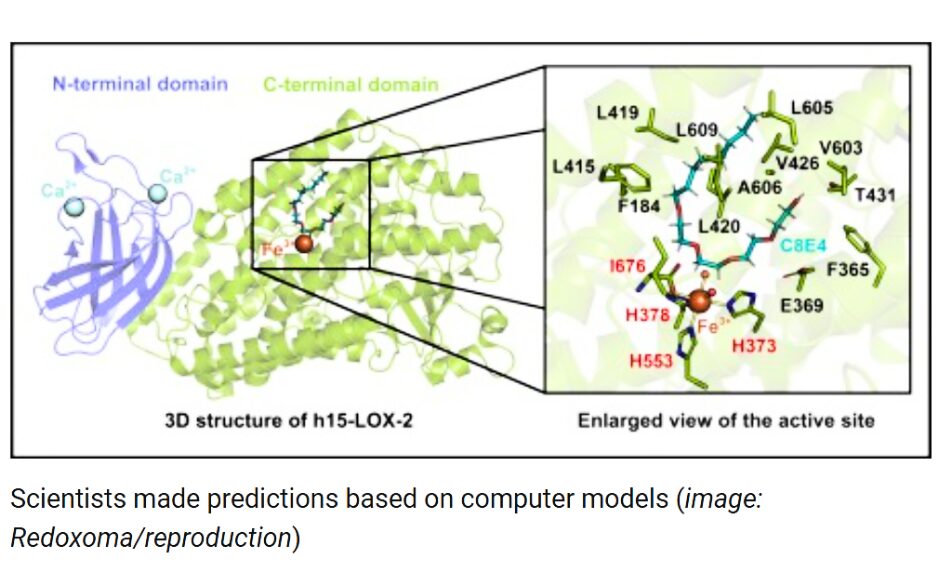
Using computational tools and virtual screening, researchers at the Center for Redox Processes in Biomedicine (Redoxoma) have identified new inhibitors of the enzyme human 15-lipoxygenase-2 (h15-LOX-2). This protein plays an important role in inflammatory and metabolic processes and contributes to cellular homeostasis.
The discovery, described in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, could open up new avenues for investigating the biological and pathological functions of the enzyme and provide promising candidates for the development of new drugs.
“Although h15-LOX-2 is a potential biological target, it’s scarcely been explored for this purpose...
Read More
In humans and other multicellular organisms, cells multiply. This defining feature allows embryos to grow into adulthood, and enables the healing of the many bumps, bruises and scrapes along the way.
Certain factors can cause cells to abandon this characteristic and enter a zombie-like state known as senescence where they persist but no longer divide to make new cells. Our bodies can remove these senescent cells that tend to pile up as we age. The older we get, however, the less efficient our immune systems become at doing so.
“In addition to no longer growing and proliferating, the other hallmark of senescent cells is that they have this inflammatory program causing them to secrete inflammatory molecules,” said Peter Adams, Ph.D...
Read More




Recent Comments