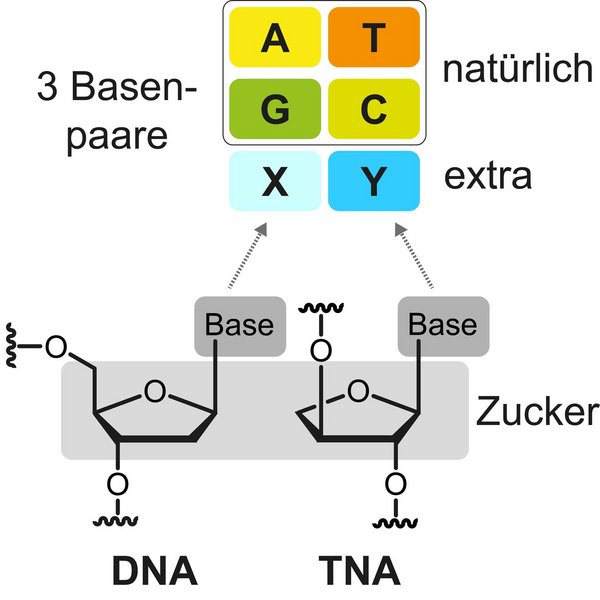
For the first time, scientists have developed artificial nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA, with several additional properties in the laboratory. The DNA carries the genetic information of all living organisms and consists of only four different building blocks, the nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of three distinctive parts: a sugar molecule, a phosphate group and one of the four nucleobases adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine. The nucleotides are lined up millions of times and form the DNA double helix, similar to a spiral staircase. Scientists from the UoC’s Department of Chemistry have now shown that the structure of nucleotides can be modified to a great extent in the laboratory.
The researchers developed so-called threofuranosyl nucleic acid (TNA) with a new, ad...
Read More






Recent Comments