
This image shows a selective actuation of the side arms of a soft robot in a horizontal uniform magnetic field. Credit: Sumeet Mishra, North Carolina State University
The ability to control the motion of soft robots, coupled with flexibility, gives them potential applications ranging from biomedical technologies to manufacturing processes. Researchers are interested in using magnetic fields to control the movement of these soft robots because it can be done remotely – the control can be exerted without physically connecting to the polymer – and because magnetic fields are easily obtained from permanent magnets and electromagnets.
A team of researchers has now found a way of embedding long chains of nanoscale magnetite particles in sheets of elastic polymer to form a magnetic polymer nanocomposite. By applying a magnetic field, the researchers can control the way the nanocomposite bends.
The process begins by dispersing nanoparticles of magnetite – an iron oxide — into a solvent. A polymer is then dissolved into the mixture, which is poured into a mold to form the desired shape. A magnetic field is then applied, causing the magnetite nanoparticles to arrange themselves into parallel chains. The solution is dried, locking the chains into place, and the finished nanocomposite can be cut, to further refine its shape. The nanoparticle chains gives an enhanced response, and by controlling the strength and direction of the magnetic field, you can control the extent and direction of the movements of soft robots.”
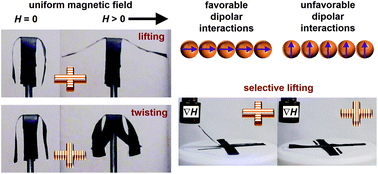
Selective and directional actuation of elastomer films utilizing magnetic anisotropy introduced by chains of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs). Under uniform magnetic fields or field gradients, dipolar interactions between the MNPs favor magnetization along the chain direction and cause selective lifting. This mechanism is described using a simple model.
“The key here is that the nanoparticles in the chains and their magnetic dipoles are arranged head-to-tail, with the positive end of one magnetic nanoparticle lined up with the negative end of the next, all the way down the line,” says Assoc Prof. Joe Tracy. “At issue is something called magnetic anisotropy, which is caused by assembling the nanoparticles into chains. When a magnetic field is applied in any direction, the chain re-orients itself to become as parallel as possible to the magnetic field, limited only by the constraints of gravity and the elasticity of the polymer.”
The researchers believe this technique may be especially attractive for some biomedical applications, as compared to soft robotics that rely on electricity or light for control. “Electrical control can raise safety issues for some medical applications,” says Mishra. “And both electrical and light signals pose challenges in terms of communicating those signals to devices embedded in the body. Magnetic fields, on the other hand, pass through easily – and pose fewer safety challenges.”
This technique uses inexpensive and widely available materials, and the process is relatively simple and easy to execute, the researchers say.
https://news.ncsu.edu/2015/12/tracy-chains-2015/






Recent Comments