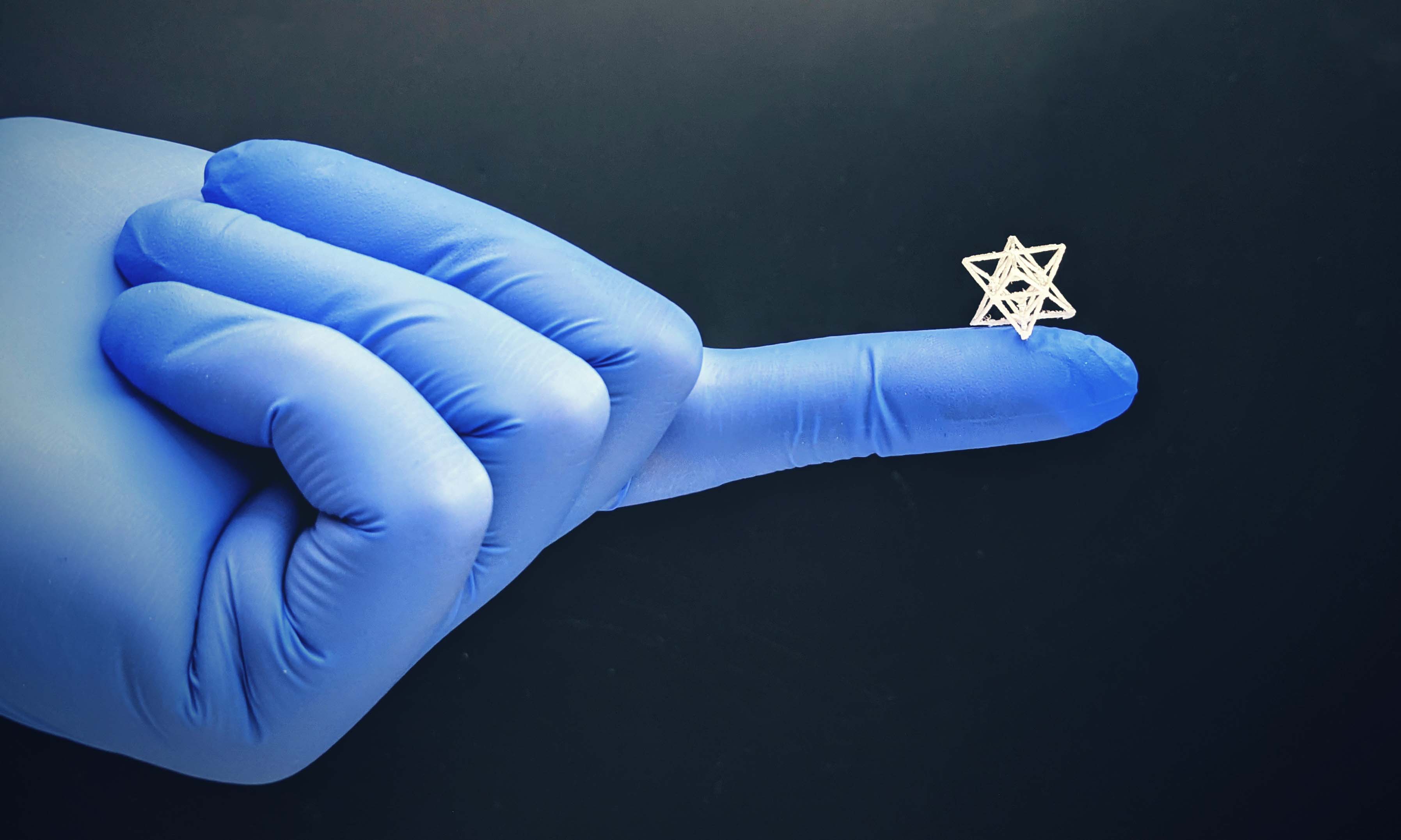

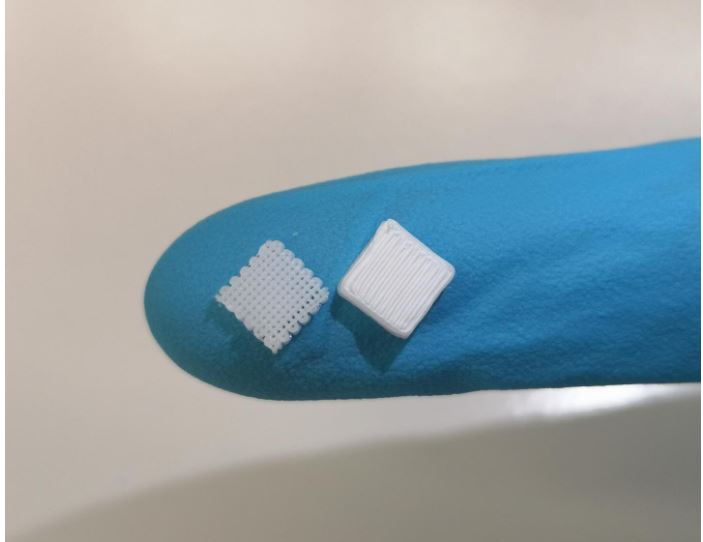
How to use glue and a high school 3D printer to create tiny implants for tissue engineering. Researchers have flipped traditional 3D printing to create some of the most intricate biomedical structures yet, advancing the development of new technologies for regrowing bones and tissue.
The emerging field of tissue engineering aims to harness the human body’s natural ability to heal itself, to rebuild bone and muscle lost to tumours or injuries.
A key focus for biomedical engineers has been the design and development of 3D printed scaffolds that can be implanted in the body to support cell regrowth.
But making these structures small and complex enough for cells to thrive remains a significant challenge.
Enter a RMIT University-led research team, collaborating with clinicians a...
Read More






Recent Comments