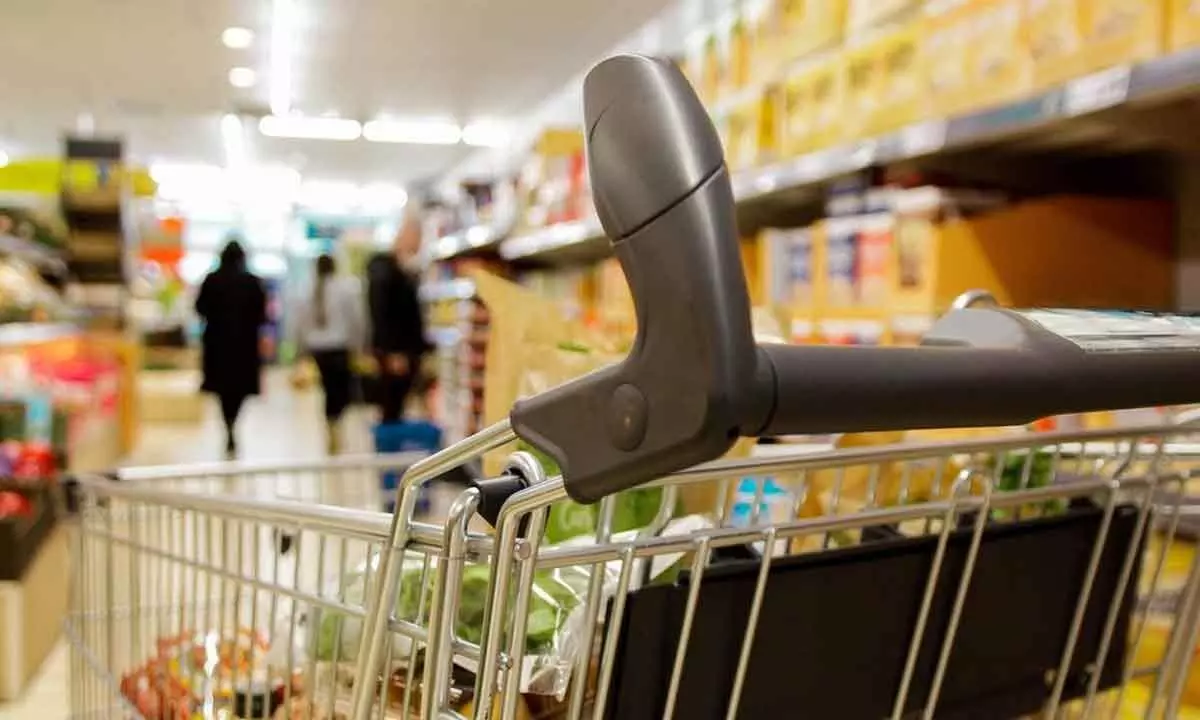

It could be the shopping trip that saves your life: supermarket trolleys are helping to diagnose atrial fibrillation which can then be treated to prevent disabling or fatal strokes. The research is presented today at ACNAP 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).
“This study shows the potential of taking health checks to the masses without disrupting daily routines,” said study author Professor Ian Jones of Liverpool John Moores University, UK. “Over the course of two months, we identified 39 patients who were unaware that they had atrial fibrillation...
Read More





Recent Comments