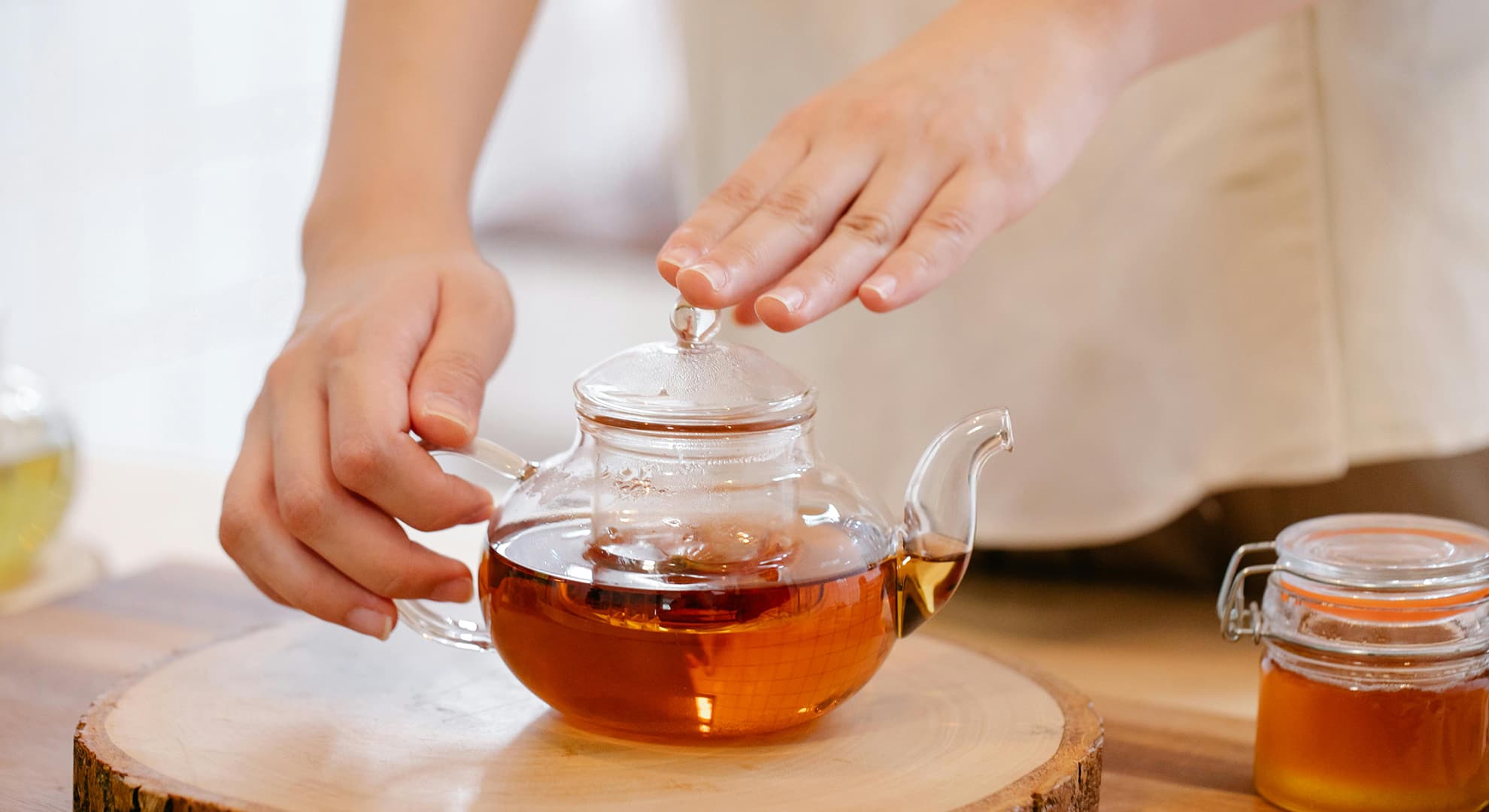

Higher intakes of black tea, berries, citrus fruits and apples could help to promote healthy ageing, new research has found.
This study conducted by researchers from Edith Cowan University, Queen’s University Belfast and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, found that foods rich in flavonoids could help to lower the risk of key components of unhealthy ageing, including frailty, impaired physical function and poor mental health.
“The goal of medical research is not just to help people live longer but to ensure they stay healthy for as long as possible,” ECU Adjunct Lecturer Dr Nicola Bondonno said.
“We know from previous research that people who have a higher flavonoid intake tend to live longer, and they are also les...
Read More





Recent Comments