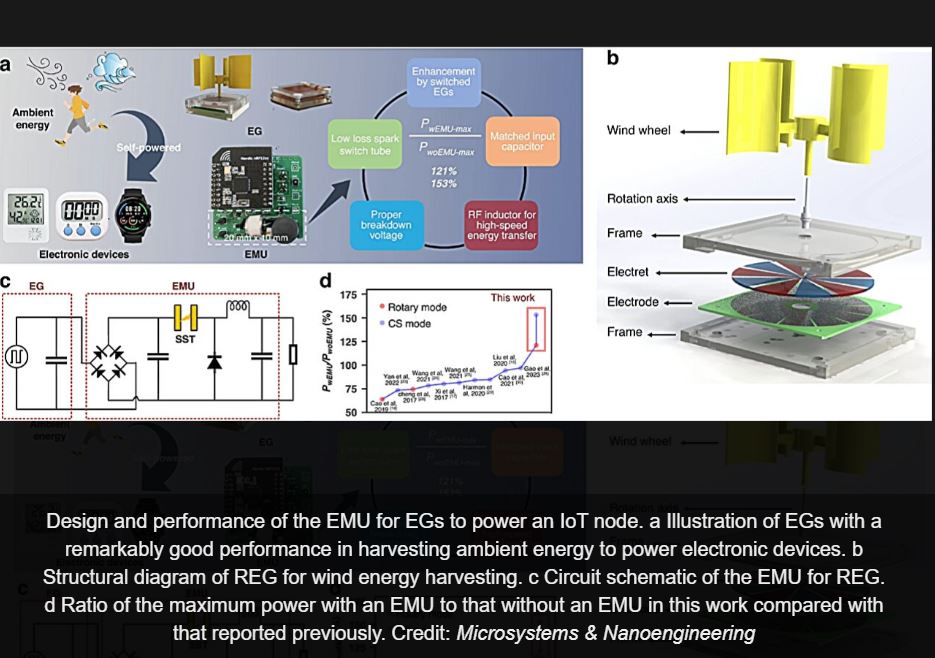
Researchers have developed a high-performance energy management unit (EMU) that significantly boosts the efficiency of electrostatic generators for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. This breakthrough addresses the challenge of high impedance mismatch between electrostatic generators and electronic devices, unlocking new possibilities for ambient energy harvesting.
Electrostatic generators have emerged as a promising solution for powering low-power devices in Internet of Things (IoT) networks, utilizing energy from environmental sources such as wind and human motion. Despite their potential, the effectiveness of these generators has been hampered by an impedance mismatch when connected to electronic devices, leading to low energy utilization efficiency.
A study published in ...
Read More







Recent Comments