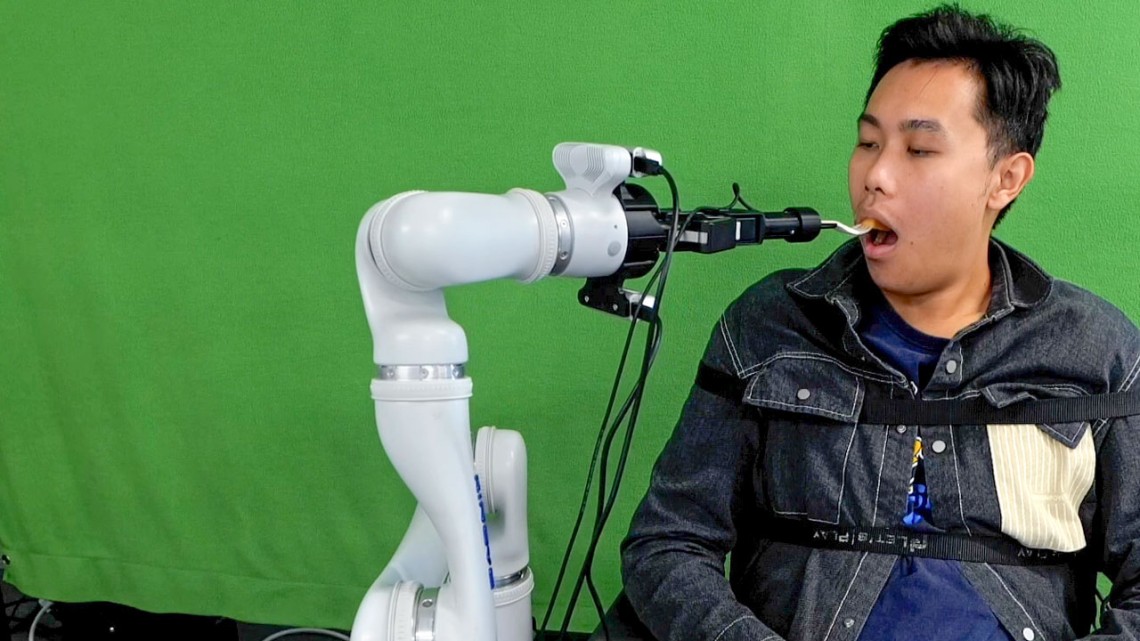
Cornell researchers have developed a robotic feeding system that uses computer vision, machine learning and multimodal sensing to safely feed people with severe mobility limitations, including those with spinal cord injuries, cerebralpalsy and multiple sclerosis.
“Feeding individuals with severe mobility limitations with a robot is difficult, as many cannot lean forward and require food to be placed directly inside their mouths,” said Tapomayukh “Tapo” Bhattacharjee, assistant professor of computer science in the Cornell Ann S. Bowers College of Computing and Information Science and senior developer behind the system...
Read More







Recent Comments