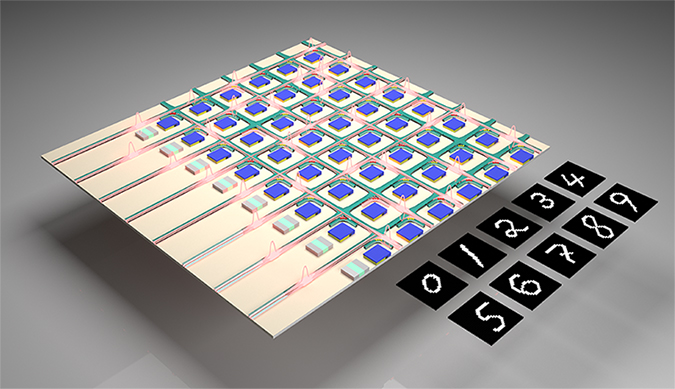
A research team has developed an optical computing system for AI and machine learning that not only mitigates the noise inherent to optical computing but actually use...
Read More

A research team has developed an optical computing system for AI and machine learning that not only mitigates the noise inherent to optical computing but actually use...
Read More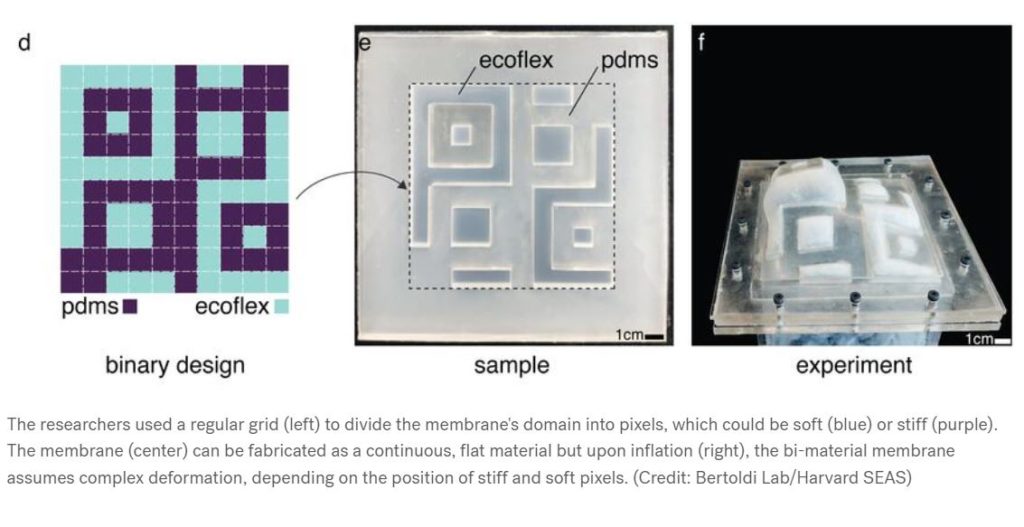
New platform can program the transformation of 2D stretchable surfaces into specific 3D shapes. Flat materials that can morph into three-dimensional shapes have potential applications in architecture, medicine, robotics, space travel, and much more. But programming these shape changes requires complex and time-consuming computations.
Now, researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have developed a platform that uses machine learning to program the transformation of 2D stretchable surfaces into specific 3D shapes.
“While machine learning methods have been classically employed for image recognition and language processing, they have also recently emerged as powerful tools to solve mechanics problems,” said Katia Bertoldi, the Wil...
Read More
A novel algorithm allows for efficient and accurate verification of quantum devices. Technologies that take advantage of novel quantum mechanical behaviors are likely to become commonplace in the near future. These may include devices that use quantum information as input and output data, which require careful verification due to inherent uncertainties. The verification is more challenging if the device is time dependent when the output depends on past inputs...
Read More
A new study by the Oregon State University College of Engineering shows that machine learning techniques can offer powerful new tools for advancing personalized medicine, care that optimizes outcomes for individual patients based on unique aspects of their biology and disease features.
The research with machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence in which computer systems use algorithms and statistical models to look for trends in data, tackles long-unsolvable problems in biological systems at the cellular level, said Oregon State’s Brian D. Wood, who conducted the study with then OSU Ph.D. student Ehsan Taghizadeh and Helen M. Byrne of the University of Oxford.
“Those systems tend to have high complexity — first because of the vast number of individual ce...
Read More
Recent Comments