
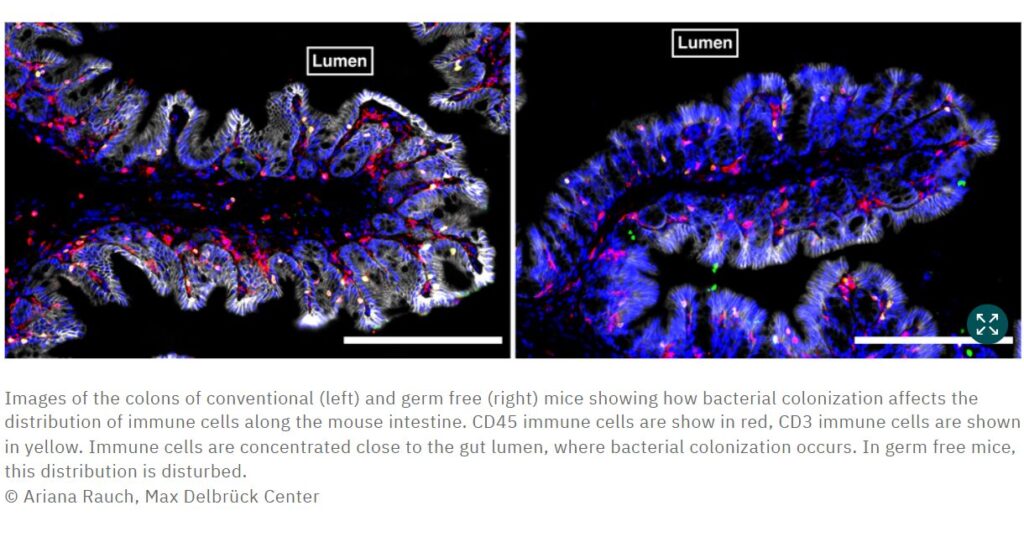
Red meat has been a part of diets worldwide since early man. It is an excellent source of protein, vitamins (such as B vitamins) and minerals (such as iron and zinc). However, red meat has long been associated with increasing the risk of heart disease, cancer and early death. What may not be so well known is the link between red meat consumption and type 2 diabetes.
A paper published in The Lancet in September 2024 highlighted this link to type 2 diabetes using data from the Americas, the Mediterranean, Europe, south-east Asia and the Western Pacific (20 countries included).
This recent study, with nearly 2 million participants, found that high consumption of unprocessed red meat, such as beef, lamb and pork, and processed meat, such as bacon, sa...
Read More




Recent Comments