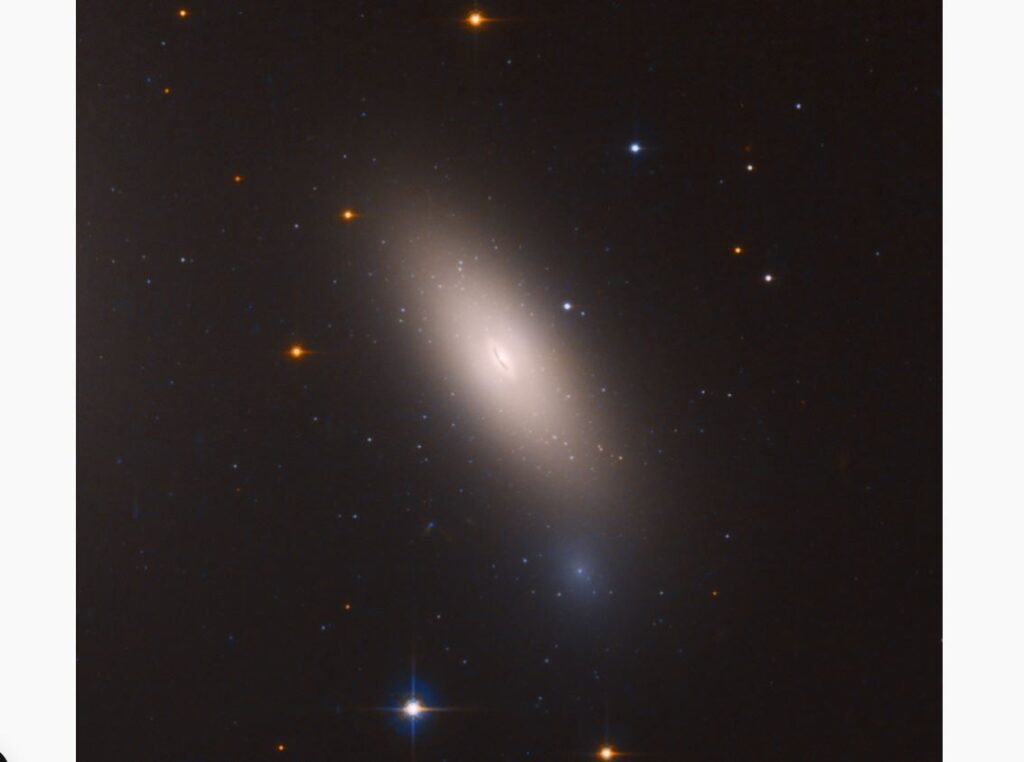

A team of scientists, led by the researcher at the IAC and the University of La Laguna (ULL) Sebastién Comerón, has found that the galaxy NGC 1277 does not contain dark matter. This is the first time that a massive galaxy (it has a mass several times that of the Milky Way) does not show evidence for this invisible component of the universe. “This result does not fit in with the currently accepted cosmological models, which include dark matter” explains Comerón.
In the current standard model cosmology massive galaxies contain substantial quantities of dark matter, a type of matter which does not interact in the same way as no...
Read More





Recent Comments