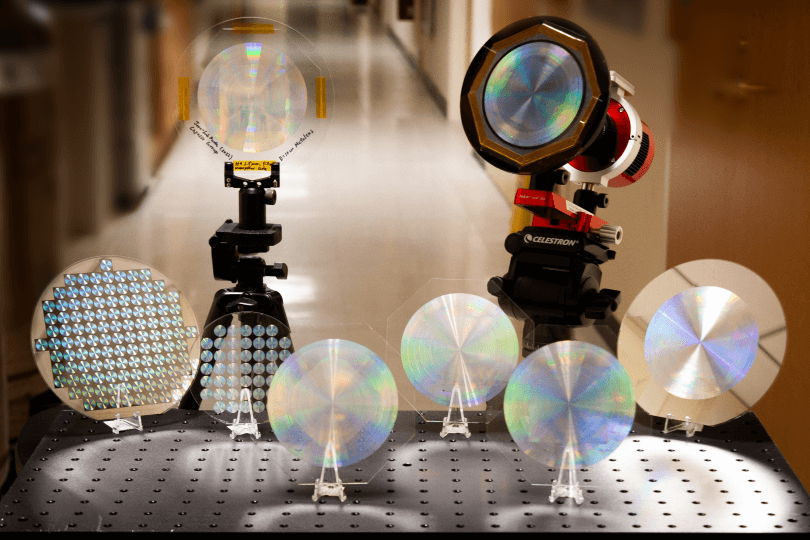
Metalenses have been used to image microscopic features of tissue and resolve details smaller than a wavelength of light. Now they are going bigger.
Researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have developed a 10-centimeter-diameter glass metalens that can image the sun, the moon and distant nebulae with high resolution.
It is the first all-glass, large-scale metalens in the visible wavelength that can be mass produced using conventional CMOS fabrication technology.
The research is published in ACS Nano.
“The ability to accurately control the size of tens of billions of nanopill...
Read More





Recent Comments